Two types of agents are used:Radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging agent either Technetium-99 or Thalliumallows measurement of blood flow through myocardiumPharmacologic stress agent Adenosine or Dipyridamole [Persan
See also: General anesthesia Paralytic agentsSeries of actions rapidly causing loss of consciousness and muscle tone, facilitating tracheal intubation.Indications Respiratory failure, w
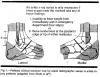
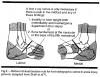
If right elbowPlace patient's right elbow at 120 degrees slightly flexedPlace left hand on forearm, apply traction away from elbowPlace right hand on upper arm with right thumb on olecranon, fingers curled around bicepsApply count
Optimal time for suture removalLocation# of daysEyelids3Neck3-4Face5Chest and upper extremities7-10Scalp7-14Lower extremities10
DrugUsual doseRenal dosingAmoxicillin500-1000 mg PO TIDEGFR >30: no changeEGFR 10-30: 250-500 mg PO q12hEGFR <10: 250-500 mg PO q12-24hHD: 250-500 mg po q12-24hPD: 250-500
See
Serous cystadenomas
Granulosa cell tumors
Dysgerminomas
Sertoli-Leydig tumors
Mature teratomas (dermoid cysts)
Etiologies
Infiltrative diseases
Sarcoidosis (non-reversible, tx w/steroids)
Amyloidosis
Scleroderma (non-reversible, tx w/ster
See also: Ottawa knee, ankle, and foot rulesSensitivity 93-100% for ankle fractures and 44-54% specific.Sensitivity 83-100% for foot fractures and 75-83% specific. Download reference article
Glasgow Coma Scale GCS according to Advanced Trauma Life Support ATLS Student Course Manual 10ed 2018 Eye OpeningNoneTo pressureTo soundSpontaneousORNT--Non-testable Verbal ResponseNone
Hx
Untreated steptococcal pharyngitis
Developing nations due to lack of access to antibiotics
Sx
New murmur
Cardiac failure
Polyarthritis
&nbs
Risk factors for Coronary Heart Disease CHDCHD risk equivalents same risk as patients with established coronary artery disease or prior MINoncoronary atherosclerotic disease e.g. carotid stenos
To be considered low risk all criteria must be met: Infant appears well no signs of toxicity No skin, soft tissue, bone, joint, or ear infection Previously health infantTerm birthNo perinatal
Rocky Mountain spotted fever RMSF is:Rapidly progressive and can be fatalEndemic throughout the US and the Americas andDifficult to diagnose but critical to treat early. RMSF is the most severe spotted fever rickettsiosis S
"When your back hurts, you may find it difficult to do some of the things you normally do. Mark only the sentences that describe you today."Scoring the RMDQ.The RMDQ is scored by adding up the number of items checked by the patient. The s
Key things:<28 weeks: visits every 4 weeks If antibody screen positive: Order Anti-D titres Consult Ob/Gyn/Perinatologis
Measles RubeolaGerman Measles RubellaRoseolaProdrome - URTI symptoms including conjunctivitisRash starts day 2-6Begins at hairline, faceSpreads to trunk and extremities over 72 hours