Source: Academic Life in Emergency Medicine
NEXUS (National Emergency X-radiography Utilization Study):
A patient’s neck can be clinically cleared safely without radiographic imaging if all five low-risk conditions are met:
- No posterior midline neck pain or tenderness
- No focal neurological deficit
- Normal level of alertness
- No evidence of intoxication
- No clinically apparent, painful distracting injury*
* Defined as “a condition thought by the clinician to be producing pain sufficient to distract the patients from a second (neck) injury. Examples may include, but are not limited to the following:
- Long bone fracture,
- A visceral injury requiring surgical consultation,
- A large laceration, degloving injury, or crush injury,
- Large burns, or
- Any other injury producing acute functional impairment
Physicians may also classify any injury as distracting if it is thought to have the potential to impair the patient’s ability to appreciate other injuries.
Canadian C-spine Rules:
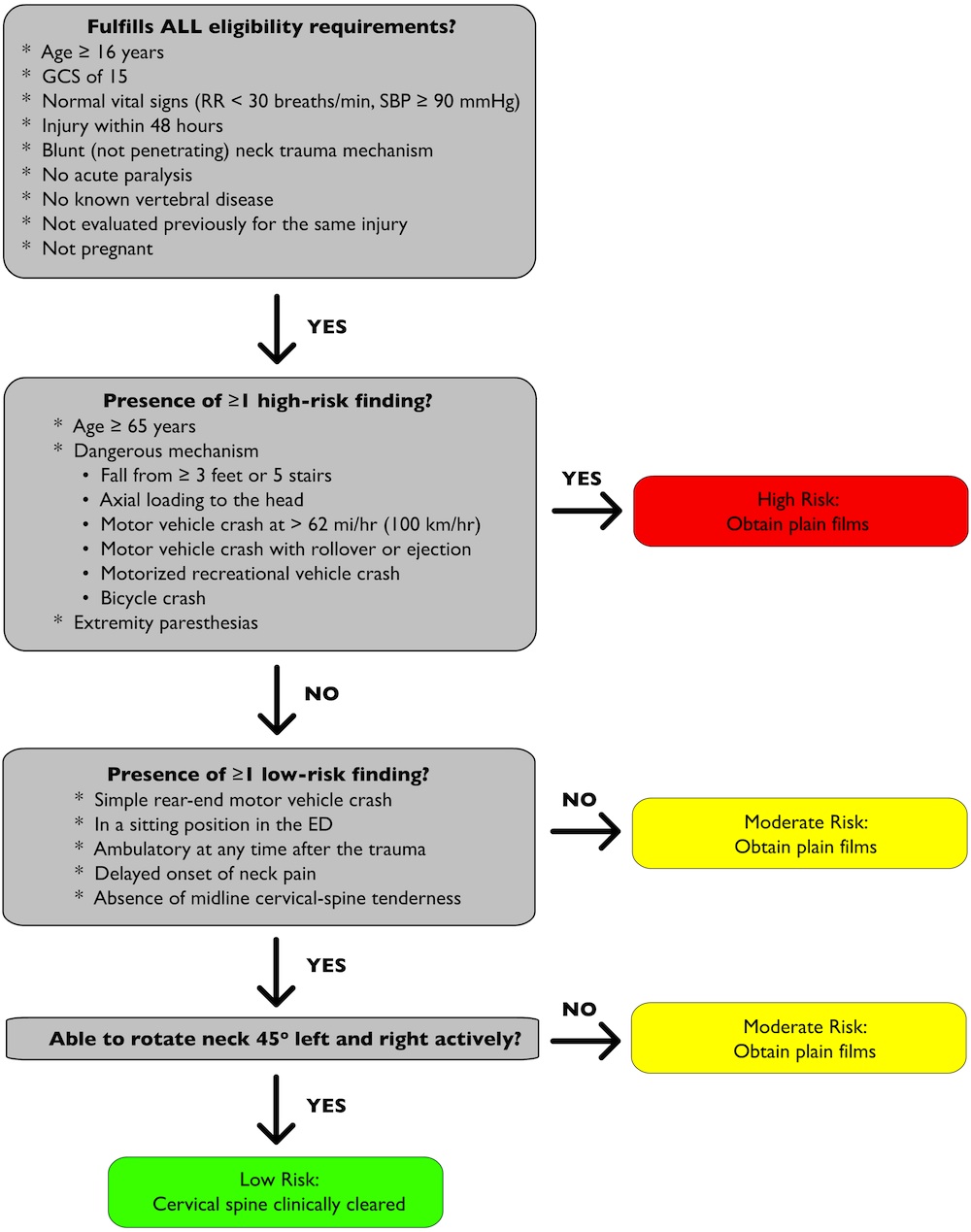
Note:
Often physicians go straight to CT imaging of the c-spine for patients with neck tenderness and moderate/high-risk findings.
NEXUS and Canadian C-spine Rules (CCR)
Hoffman JR, et al. NEJM 2000; 343: 94-9;
Stiell IG et al. JAMA. 2001 Oct 17;286(15):1841-8.
Ability to detect clinically significant c-spine injury:
Sensitivity Specificity
NEXUS study 99.6% 12.6%
CCR Study 99.4% 45.1%
