What do people grieve?
- Death
- Dying
- Family member dying
- Friend dying
- Pet dying
- Separation and divorce
- Dementia
- Loss of job
- Loss of place/identity
- Loss of future plan
- Diagnosis of self, family member, child
What is normal grief (common reactions)?
- Shock (apathy, numbness, blankness, despair, lack of emotion/reaction)
- Disbelief or incredulity
- Anger
- Sadness, helplessness, hopelessness, tears
- Guilt and shame
- Behavioural disorganization
- Restlessness
- Tension
- Irritability
- Loss of interest in typical activities
- Loss of interest in people one cares for
- Impairment of work performance
- Pining
- Preoccupation with thoughts of the loss to the exclusion of other more typical thoughts
- Sense of continued presence of the deceased
- Inability to form new attachments
- Somatic complaints
- Headaches
- Digestive complaints
- Muscle aches and pains
The Kübler-Ross 5 stages of grief and loss:
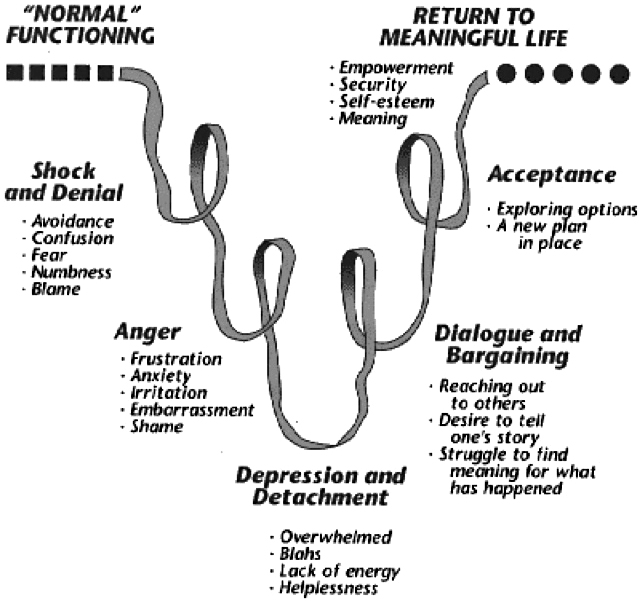
Tasks of grief
- Acknowledge the loss
- Emotionally and intellectually
- Experience the pain of the loss
- Have common reactions
- Process positive AND negative feelings about the lost object/person
- Adjust to the new environment
- Assume tasks person used to do
- Memorialization
- Find a way to keep memories alive (spirit with you) while moving forward
Grief Counselling
- Assists with the natural, normal, healthy grieving process
- Accepting the loss
- Talk about the details of the death and mourning process
- Help identify and express feelings
- Problem solve to assist with adjustment to new circumstances (brainstorm options)
- Encourage continued bond
- Discourage avoidance, distraction, rebound replacement
- Provide information about normal grieving
- Flexibility of time needed
- Process of ups and downs
- Anniversaries difficult
- Provide ongoing support
- Note productive coping (e.g. deciding to decrease workload while grieving)
- Note interfering defences (e.g. taking on excessive amounts of work, substance use)
- Avoid platitudes (e.g. I know how you feel. You're holding up well.)
Grief Therapy
- Resolves complications in the grief process
- Those who are "stuck"
- Traumatic death
- Conflicted relationships
- Mental illness or personality disorders
- Pre-existing or arising from
- Masked grief
- Behavioural, psychological, or somatic symptoms
