Frequently recheck the posterior oropharynx for signs of posterior bleeding
- Ask the patient to swallow to identify old vs new blood
Be careful with silver nitrate or cautery. You can easily cause a permanent septal perforation.
If difficult to control with usual techniques:
- Tranexamic acid 1 g IV
- Deeply pack with vaseline-soaked gauze, may need to tie lengths together
- Special devices:
- Merocel nasal tampon
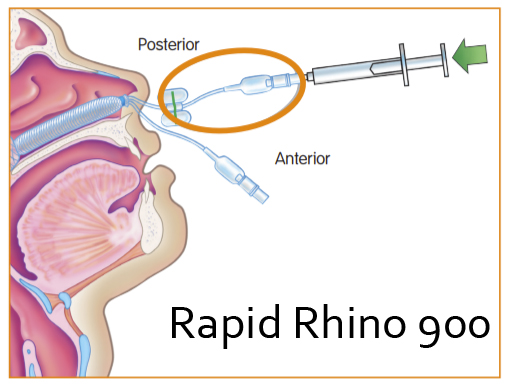
- Rapid Rhino
-
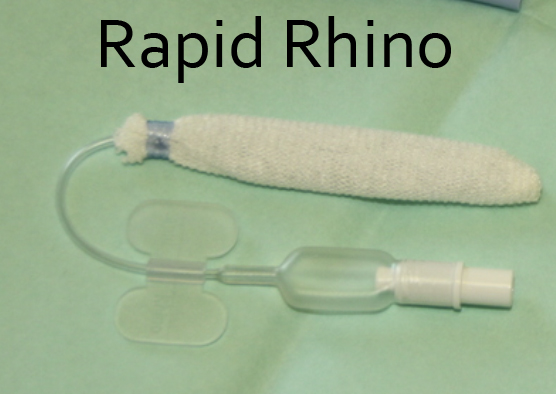
- Note it also comes in a dual lumen model, click here for the infosheet as a PDF [1.54 MB]
-
- Epistax
-
- "Made from soft, medical-grade silicone for patient comfort. Beveled posterior tip and soft silicone construction allow for easy placement and prevents adhesion for easy removal. Designed to control intranasal bleeding with a two-balloon epistaxis catheter: Small balloon controls posterior bleeding. Large balloon controls anterior bleeding. The Epistax Epistaxis Balloon Catheter is available with or without an inflation syringe. The optional syringe is used to expand the balloons with normal saline. The volume of saline injected determines the size and pressure of the balloons, resulting in a controlled, uniform pressure to manage bleeding. The integral airway tube allows for nasal breathing while the balloons are inflated." -Medline (Supplier page)
-
Out patient:
- Tranexamic acid 500 mg to 1000 mg TID-QID prn
- Otrivin i spray per nostril q8h
 ]
]