Source: Academic Life in Emergency Medicine
Potassium regulation
1. Internal K shift: modulated by insulin, catecholamines, acid-base status
2. Total body K elimination: By kidney (95%) and gut (5%)
Adverse effects of hyperkalemia
1. Cardiac: Peaked T, wide QRS, loss of P wave, sine wave; although Vfib may be first cardiac manifestation.
2. Neuromuscular: Paresthesias, weakness
3. Metabolic: Mild hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis
Goals of hyperkalemia treatment
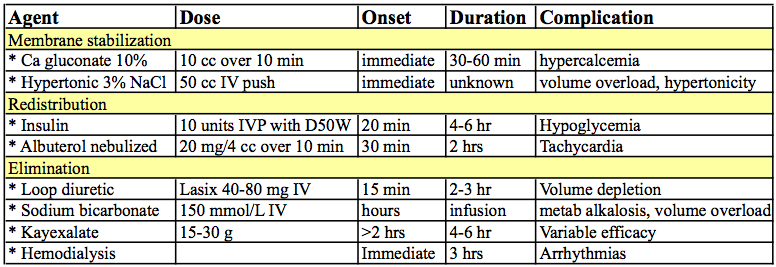
1. Cardiac membrane stabilization
* Calcium: Reduces threshold potential in myocytes; check to be sure not on digoxin
* Hypertonic saline: Only for severe hyponatremia in setting of hyperkalemia
2. K redistribution
* Insulin: Drives K intracellularly and drops serum K level by 0.6 mmol/L
* Beta-agonist: Drives K intracellularly and 10 mg albuterol drops serum K level by 0.6 mmol/L (20 mg --> K drops by 1 mmol/L); effective in only 60% of patients
3. K elimination via kidney/gut
* Bicarbonate: drives K out at distal nephron; best as infusion x 4-6 hrs
* Loop diuretic
* Exchange resin (sodium polystyrene sulfonate) – case reports of colonic necrosis; constipating med and so combined with sorbitol; minimal benefit.